Minimal Promoters:
Minimal promoters are used when they are well characterized and proven to result in high levels of expression in the cell type indicated. Expression cassettes are cloned into the promoter plasmid using standard cloning techniques. Following pronuclear injection of the minimal promoter transgene into fertilized oocytes, founder animals should express the gene product in an expression pattern similar to the gene whose promoter is controlling it.
| minimal promoter | size | reference |
| αMHC | 6 kb | http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2026617 pJG/ALPHA MHC was a gift from Jeffrey Robbins (Addgene plasmid # 55594) |
BAC Recombineering:
Bacterial artificial chromosomes (BACs) are cloning vectors (7-12 kb) containing 150-250 kb of genomic DNA. Because of the large size of insert, most BACs contain genes in their entirety including any cis-regulatory elements. By using recombineering methodologies, we are able to insert our expression cassette under control of the promoter of a particular gene. Following pronuclear injection of the BAC transgene into fertilized oocytes, founder animals should express the gene product in an expression pattern similar to the gene whose promoter is controlling it.
Construction of BAC transgenes (as an example, the generation of acta2-optoα1AR-IRES-lacZ is given):
a) Construction of the target vector: A BAC containing the promoter of interest is obtained and used as a template for PCR amplification of arm 1 and arm 2. Arms 1 and 2 are typically 500-700 bp long and are derived from the genomic sequence immediately upstream and downstream respectively of the initiation codon of the gene (in this case the initiation codon is in exon 2). Arms 1 and 2 are cloned into the target vector flanking the expression cassette.
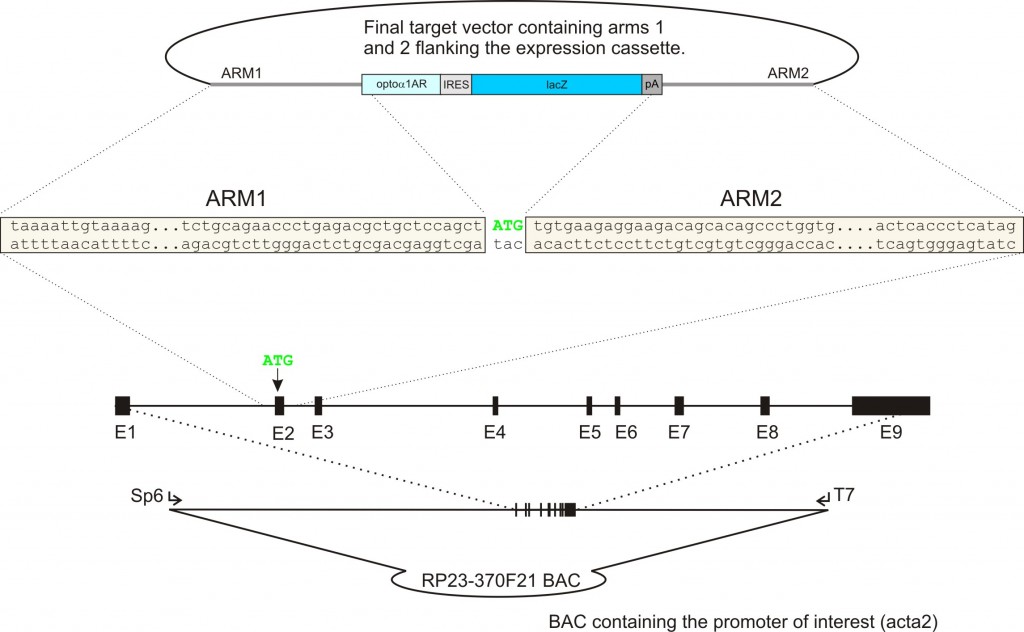
b) Homologous recombination: The insert is purified from the target vector and used to transform bacteria carrying the BAC. Recombination enzymes are activated and homologous recombination occurs between the BAC and the target vector.
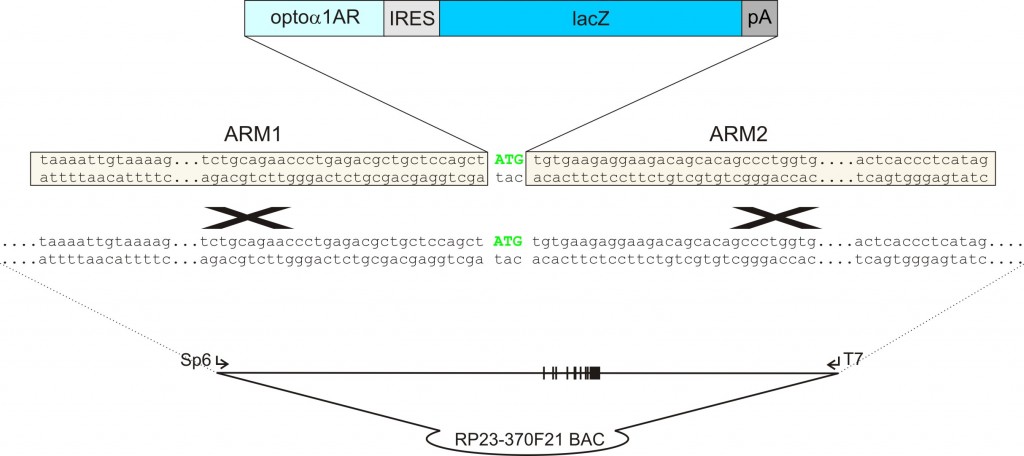
c) The resulting construct is the final transgene construct where the expression cassette has replaced the initiation codon in the BAC.
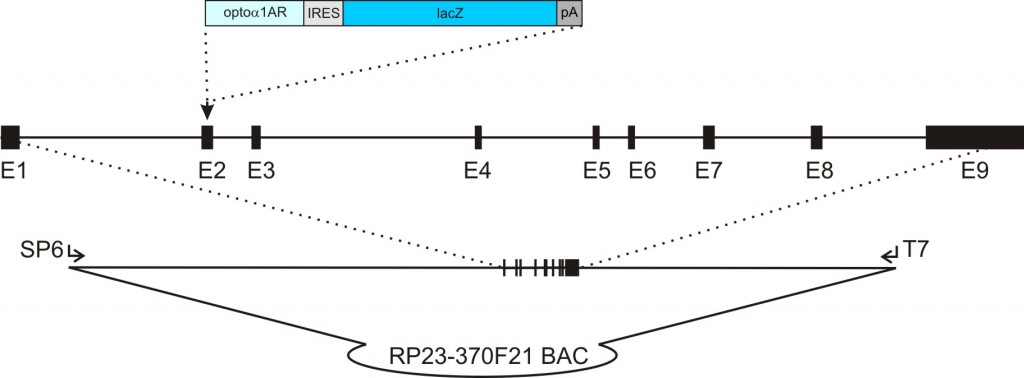
acta2-opto-α1AR-IRES-lacZ transgenic construct
